Understanding Occult Hepatitis B Infection (OBI): Insights and Diagnostic Solutions
Occult hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection (OBI) refers to the presence of HBV DNA in the absence of detectable hepatitis B surface antigen[1]. This enigmatic condition poses a considerable challenge for clinicians, as the virus remains hidden, making its detection and subsequent management a complex task.
This article will explore Occult Hepatitis B Infection, its key characteristics, clinical significance, and the challenges associated with its detection.

Key Characteristics of Occult Hepatitis B Infection
Occult Hepatitis B Infection (OBI) presents a perplexing challenge to healthcare professionals due to its distinct characteristics, which set it apart from more overt forms of hepatitis B. Therefore, further research and exploration are critical. Here is a detailed explanation of the characteristics:
- Low-Level HBV DNA
At the heart of Occult Hepatitis B Infection lies its elusive nature, primarily characterized by low levels of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA circulating in the bloodstream. Unlike typical hepatitis B infections where the viral DNA is abundant and easily detectable, OBI operates stealthily with a minimal viral load. This low-level presence of HBV DNA poses a significant hurdle to traditional diagnostic methods, contributing to the underdiagnosis of Occult Hepatitis B Infection. The subtlety of this infection makes it imperative for healthcare providers to adopt more sensitive tools to identify the virus accurately.
- Clinical Significance
Despite its discreet manifestation, OBI holds substantial clinical significance. The persistence of low-level HBV DNA in the liver, even when surface antigen tests indicate negativity, can lead to severe consequences.
Research on the prevalence of Occult Hepatitis B virus infection in adults concludes that a substantial proportion of people carry occult HBV infection, especially among high-risk groups[2]. OBI has been proven to be associated with end-stage liver diseases, hepatocellular carcinoma, in particular. Chronic OBI may lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. OBI can be reactivated and replicated for the previous HBV infection or carriers who have received immunosuppressive or chemotherapy[3].
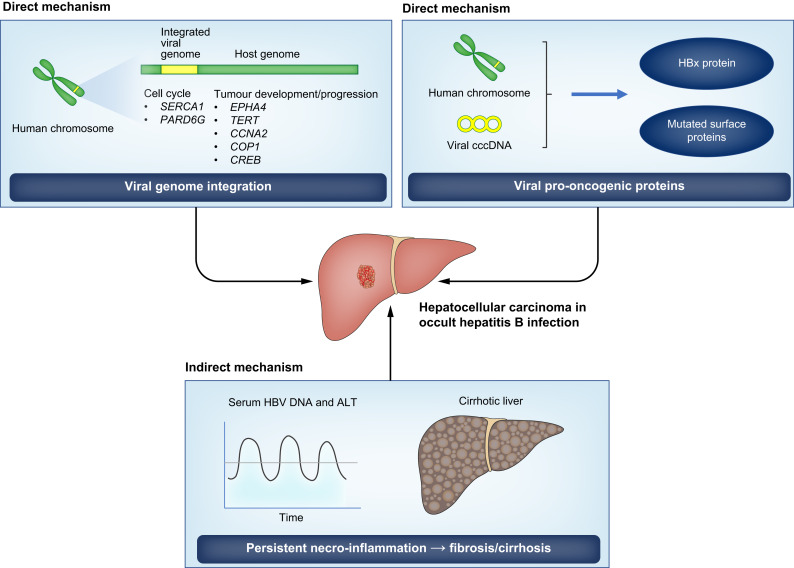
Copyright picture from https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278%2820%2930357-3/fulltext#gr3
- Diagnostic Challenges
Technically, the most direct diagnostic method is the detection of replicative HBV DNA within liver tissue. However, it is hard to manipulate due to the difficulty of obtaining liver tissue specimens and extracting pure HBV DNA fragments in liver tissue for OBI diagnosis, as well as the lack of standardized analytical methods. Therefore, the detection of replicative HBV DNA in liver tissue is not suitable for routine clinical practice.
On the other hand, the presence of HBcAb (antibodies against hepatitis B core antigen) in the blood only indicates that the patient has been infected with HBV. Further, HBV DNA detection is required for the diagnosis of OBI. Additionally, a portion (20%) of OBI patients may have negative HBcAb results. Serum HBcAb testing can only distinguish the majority (but not all) of individuals with prior HBV infections[4].
Consequently, a common diagnostic method for OBI is the detection of HBV DNA in blood. Since OBI patients typically have very low levels of HBV DNA in their blood, developing highly sensitive nucleic acid testing methods is crucial.
Advanced Diagnostic Solutions for Occult Hepatitis B Infection
In light of these challenges, healthcare providers are increasingly recognizing the importance of advanced diagnostic solutions for the accurate identification of OBI. The limitations of standard methods highlight the critical role played by innovative detection tools, such as the Sansure Hepatitis B Virus DNA QuantitativeFluorescence Diagnostic Kit, in addressing the complexities associated with Occult Hepatitis B Infection diagnosis.
Key Features of Sansure’s Diagnostic Kit:
- Sensitivity: The kit adopts advanced magnetic beads technology, allowing its high sensitivity (5 IU/mL) and ensuring a low false negative rate.
- Specificity: Sansure’s diagnostic solution is highly specific to HBV DNA, minimizing the risk of false positives or negatives.
Applications of Sansure’s Diagnostic Kit:
- Early Detection: Sansure’s kit facilitates the early detection of Occult Hepatitis B Infection, enabling timely intervention and management.
- Monitoring Treatment Efficacy: The quantitative analysis allows clinicians to monitor the effectiveness of antiviral treatments and adjust strategies accordingly.
By adopting advanced diagnostic tools, healthcare professionals can better navigate the diagnostic landscape, leading to improved patient outcomes and more effective management of Occult Hepatitis B Infection.

Conclusion
Understanding and effectively managing Occult Hepatitis B Infection requires a nuanced approach. The challenges associated with low-level HBV DNA detection necessitate the adoption of advanced diagnostic solutions. The Sansure Hepatitis B Virus DNA Quantitative Fluorescence Diagnostic Kit emerges as a reliable ally in this endeavor, offering heightened sensitivity, specificity, and quantitative analysis capabilities. By recommending Sansure’s advanced diagnostic solution, healthcare professionals can enhance their ability to diagnose Occult Hepatitis B Infection accurately and take proactive measures to mitigate its clinical impact.
Reference
[1] Kwak MS, Kim YJ. Occult hepatitis B virus infection. World J Hepatol. 2014 Dec 27;6(12):860-9. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i12.860. PMID: 25544873; PMCID: PMC4269905.
[2] Yu Ri Im, MBBChir, Rukmini Jagdish, BMBS, Damien Leith, MBBS, Jin Un Kim, MBBS , Kyoko Yoshida, MD, Amir Majid, MBBS, et al. Prevalence of occult hepatitis B virus infection in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022; 7:932-942.
[3] Giovanni Raimondo, Stephen Locarnini, Teresa Pollicino, Fabien Zoulim, Anna S. Lok, and theTaormina Workshop on Occult HBV Infection Faculty Members, Update of the statements on biology and clinical impact of occult hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2019; 71:397-408.
[4] Mak LY, Wong DK, Pollicino T, et al. Occult hepatitis B infection and hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology, virology, hepatocarcinogenesis and clinical significance. J Hepatol. 2020 Oct,73(4):952-964.